Beeswax (cera alba) is a natural wax produced by honey bees of the genus Apis. Chemically, beeswax consists mainly of esters of fatty acids and various long-chain alcohols.
Uses
- Plastic
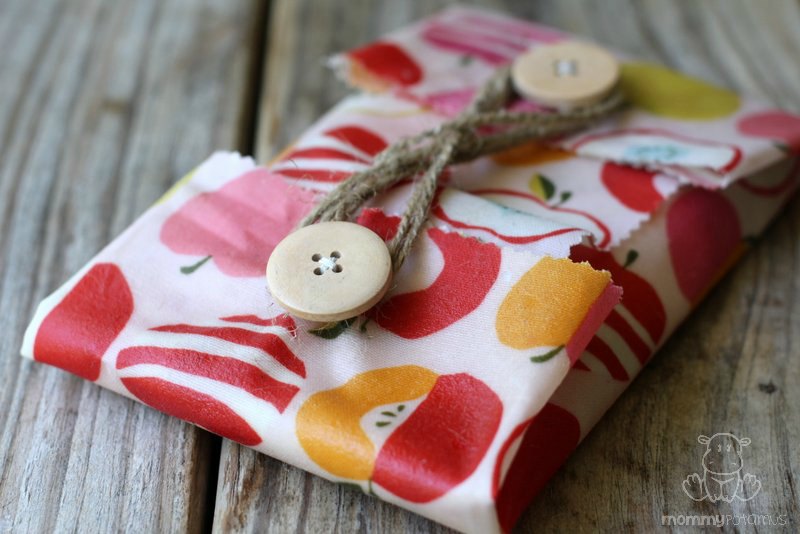
- Wrap – see featured image (by infusing cotton with beeswax, jojoba oil and tree resin)
- Candle
- Cosmetics
- As a modelling material in the lost-wax casting process, or cire perdue
- For wax tablets used for a variety of writing purposes
- In encaustic paintings such as the Fayum mummy
- Portraits
- Bow making
- To strengthen and preserve sewing thread, cordage, shoe laces, etc.
- As a component of sealing wax
- To strengthen and to forestall splitting and cracking of wind instrument reeds
- To form the mouthpieces of a didgeridoo, and the frets on the Philippine kutiyapi – a type of boat lute
- As a sealant or lubricant for bullets in cap and ball firearms
- To stabilize the military explosive Torpex (before being replaced by a petroleum-based product)
- In producing Javanese batik
- As an ancient form of dental tooth filling
- Surfboard wax,
- Lubricant for furniture joints, doors and windows,
- Used by NASA with an enzyme to mop up oceanic oil spills
- Bleed control from bone surfaces
- Surgical bone wax
- Shoe polish and furniture polish
Potential Uses
No new uses as yet identified by author’s. Your contributions welcome.
Processes
- When beekeepers extract the honey, they cut off the wax caps from each honeycomb cell with an uncapping knife or machine. Its colour varies from nearly white to brownish, but most often a shade of yellow, depending on purity, the region, and the type of flowers gathered by the bees. Wax from the brood comb of the honey bee hive tends to be darker than wax from the honeycomb. Impurities accumulate more quickly in the brood comb. Due to the impurities, the wax must be rendered before further use. The leftovers are called slumgum.
- The wax may be clarified further by heating in water. As with petroleum waxes, it may be softened by dilution with mineral oil or vegetable oil to make it more workable at room temperature.
- CAUTION – BEESWAX IS FLAMMABLE. Do not let the water boil when melting wax. If beeswax should boil over or flow onto the burner there is danger of a violent fire. When handling beeswax, low heat and careful attention are advisable
More Information
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beeswax
- http://matteroftrust.org/5044/101-uses-for-beeswax
- https://www.beeswrap.com/pages/about-us
- [Featured Image] https://images-na.ssl-images-amazon.com/images/S/aplus-seller-content-images-us-east-1/ATVPDKIKX0DER/A0252963B0X1OB20Q9CI/B00B3U0FW4/7qvbs9jfQA2Y._UX899_TTW_.jpg