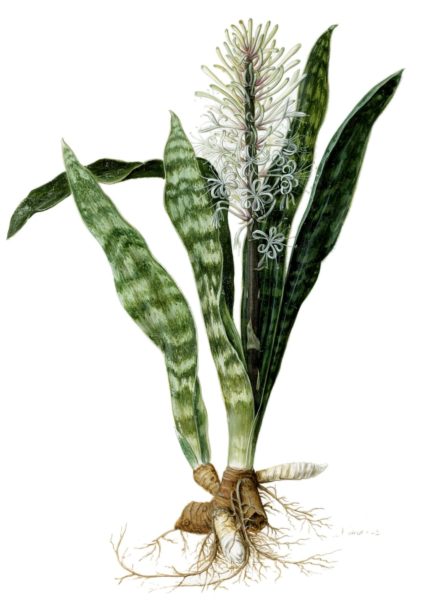
Sansevieria (snake plant, bow string hemp etc.) is a genus of about 70 species of flowering plants, native to Africa, Madagascar and southern Asia.
Sansevieria (snake plant, bow string hemp etc.) is a genus of about 70 species of flowering plants, native to Africa, Madagascar and southern Asia.
A soft, silky and elastic fibre is obtained from the leaves. Yields of up to 2.25 tonnes per hectare per year have been recorded.
Uses
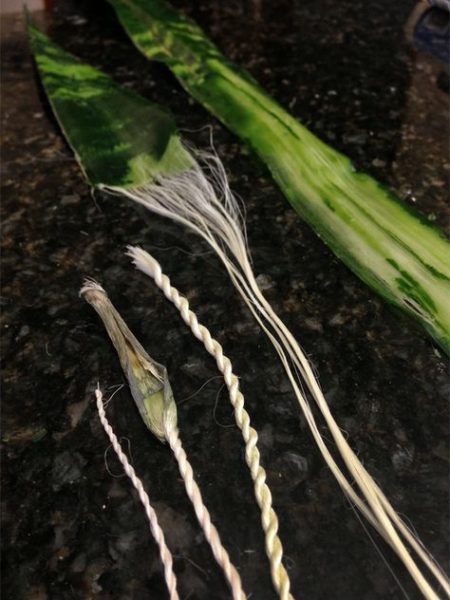

- string
- bowstrings for hunting
- thread for clothes
- nets
- mats
- fine paper
- Sansevieria ehrenbergii has sap used as antiseptic and the leaves are used for bandages in traditional first aid.
Potential Uses
- Fibre for composites
- Warning, unknown if this is safe: Surgical suture? (as may breakdown naturally)
- Contains saponins: could be used for soap?
Processes
- [Overview; need not be detailed.]
More Information
- Wikipedia
- Plants For A Future entry
- Book: Useful Fiber Plants of the World – Dodge C.R., 1897
- Ecocrop Data Sheet for Sansevieria guineensis
- Common names: English: bowstring hemp; iguanatail; mother-in-law’s tongue; snake plant. Spanish: lengua de suegra; lengua de vaca. Local Common Names: Dominican Republic: Espada de Santa Elena; Espada de Santa Teresa; Hoja de Santa Elena. Haiti: oreilles d’ane; safran; z’oreilles bourrique. Lesser Antilles: bowstring; karata; langue a chat; lash; sanddragon de cermitiere; z’oreille a bourrique. Mozambique: tchikwenga. Puerto Rico: chucho; cocuisa; lengua de chuco; sansiviera. Saint Lucia: lanng bèlmè; mother-in-law’s-tongue.